- HOME>
- EN>
- Research:
- Quantum Computing, Annealing and Optimization
Significance of the Research
- Data assimilation is a mathematical discipline that integrates observational data with numerical models to improve the interpretation and prediction of dynamic systems. It plays a crucial role in Earth sciences, particularly in Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP). Currently, many weather forecasting centers worldwide use variational methods or ensemble-variational data assimilation techniques, which iteratively minimize the cost function through gradient-based optimization. However, these methods require extensive computational resources due to their iterative minimization.
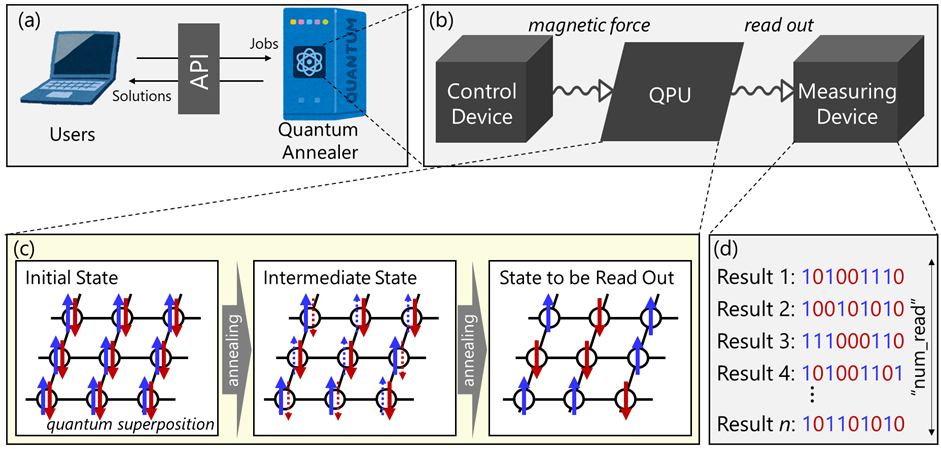
- Recently, quantum computing has emerged as a promising new computational approach, with the potential to overcome the limitations of classical computers. By leveraging quantum effects such as tunneling, superposition, and entanglement, quantum computers can significantly reduce computational demands. In particular, quantum annealing machines, developed by D-Wave (Canada), have proven to be powerful tools for solving optimization problems.
- Our laboratory is actively researching data assimilation using quantum annealing machines. We aim to realize quantum data assimilation for numerical weather prediction models by developing mathematical techniques that enhance noise resilience and minimize the required number of quantum bits.
- Beyond data assimilation, we are also exploring new applications of quantum computing in disaster prediction and mitigation, including research involving Boltzmann machines and other quantum-based methodologies.
Reference
- Kotsuki, S., Kawasaki, F. and Ohashi, M. (2024): Quantum Data Assimilation: A New Approach to Solve Data Assimilation on Quantum Annealers. Nonlin. Processes Geophys. Lett.

